Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome
Enlarged vestibular aqueduct syndrome. Pendred syndromenonsyndromic enlarged vestibular aqueduct PDSNSEVA comprises a phenotypic spectrum of sensorineural hearing loss SNHL that is usually congenital and often severe to profound although mild-to-moderate progressive hearing impairment also occurs vestibular dysfunction and temporal bone abnormalities bilateral enlarged vestibular aqueduct with or without cochlear hypoplasia. Large vestibular aqueduct syndrome LVAS also known as enlarged vestibular aqueduct EVA or large endolymphatic sac anomaly LESA refers to the presence of congenital sensorineural hearing loss with an enlarged vestibular aqueduct due to enlargement of the endolymphatic duct. The condition is also known as a dilated vestibular aqueduct or a large vestibular aqueduct.
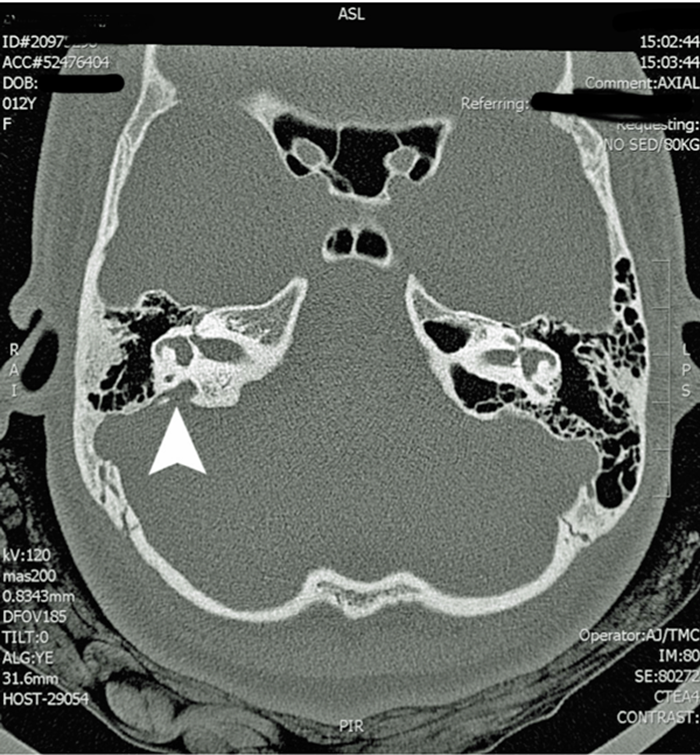
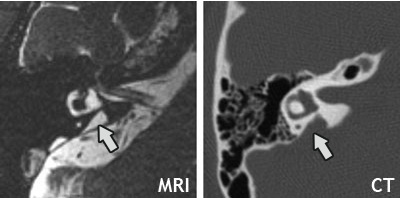
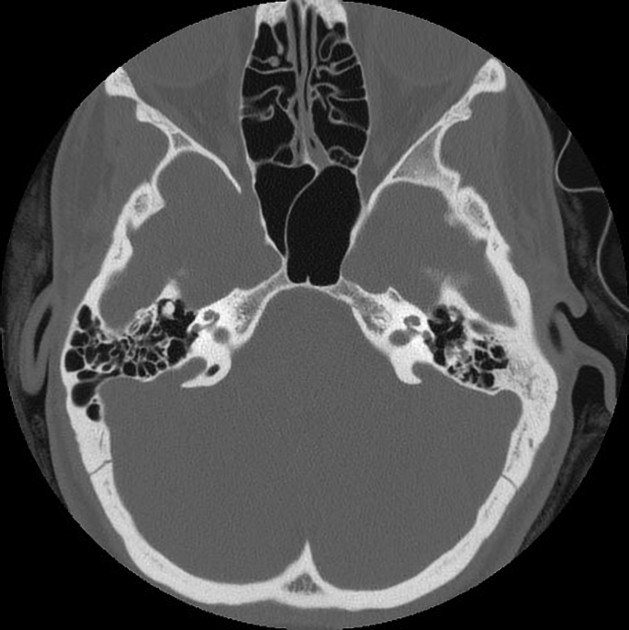
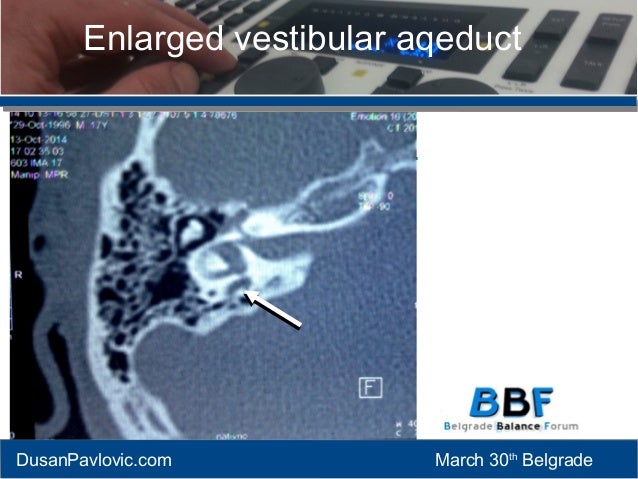
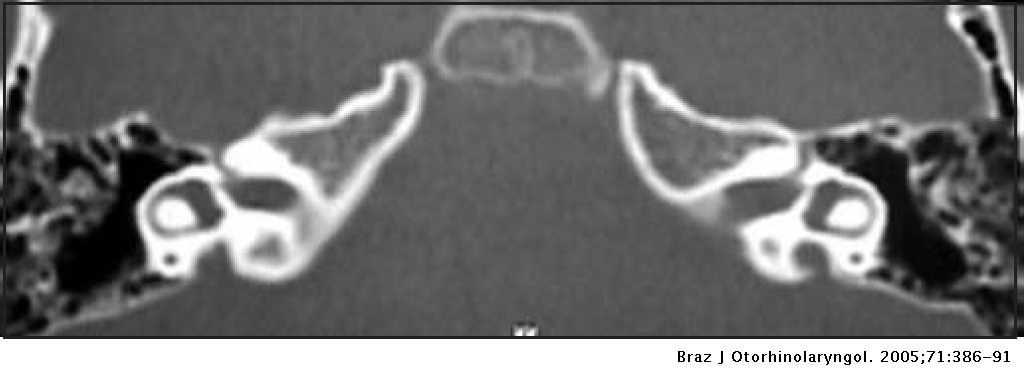
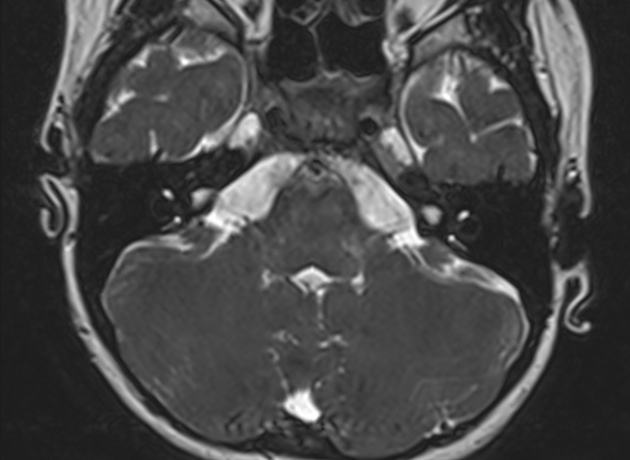
It is manifested as enlargement of the bony canal of the vestibular aqueduct on computed tomography CT or enlargement of the endolymphatic sac visualized directly on magnetic resonance imaging MRI. The association of this anatomic anomaly with SNHL led them to coin the term large vestibular aqueduct syndrome LVAS Phelps 1996. ClinicalTrialsgov lists trials that are related to Enlarged vestibular aqueduct syndrome.
Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome EVAS Also known as Large Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome EVAS is a non-congenital syndromic form of hearing loss caused by an enlarged vestibular aqueduct usually with a diameter larger than 15mm Valvassori Clemis 1978. To determine the natural history of hearing loss in children with enlarged vestibular aqueduct EVA syndrome. This is called an enlarged vestibular aqueduct or EVA.
Inner ear Vestibular Aqueduct Cochlea. Click on the link to go to ClinicalTrialsgov to read descriptions of these studies. Studies listed on the ClinicalTrialsgov website are listed for informational purposes only.
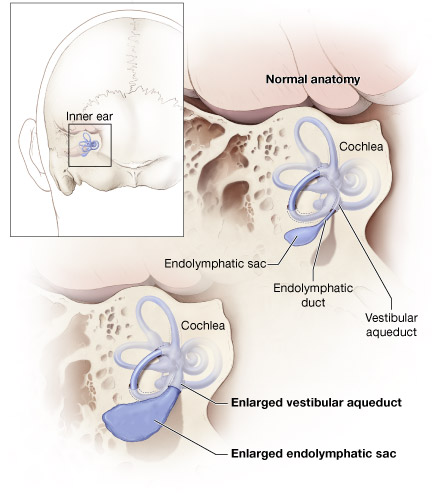
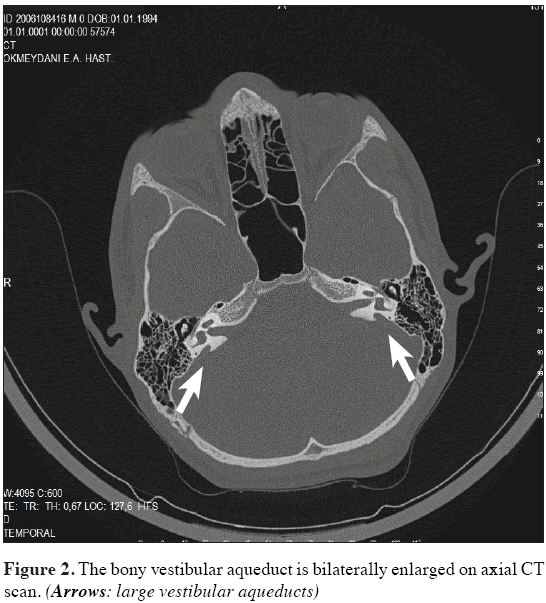
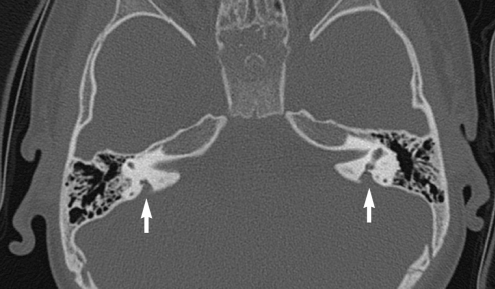
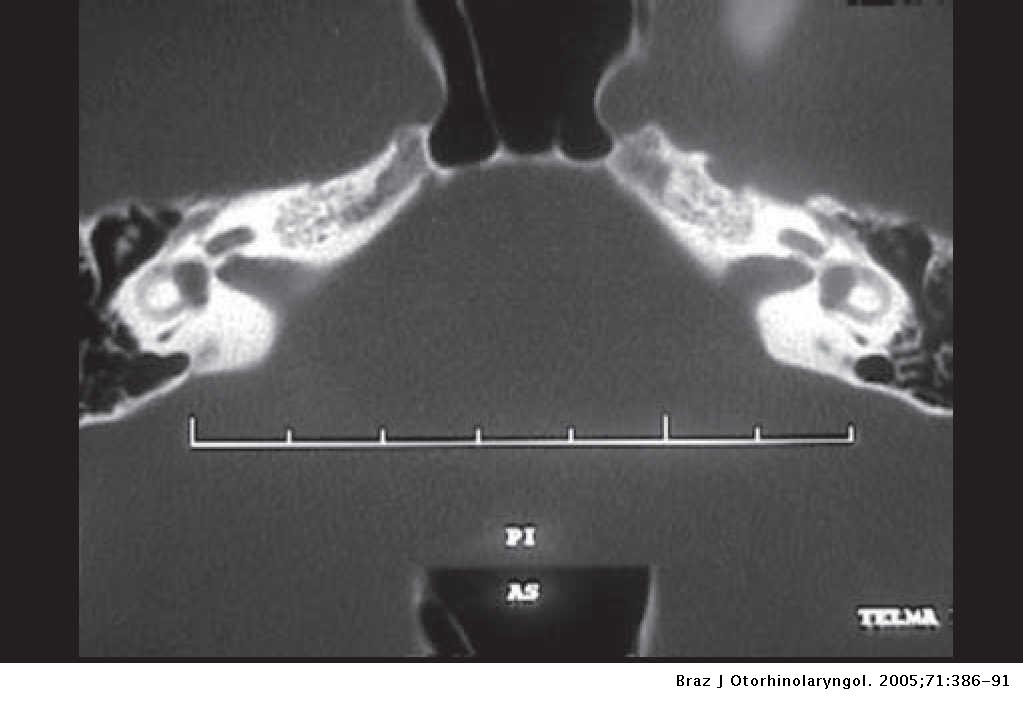
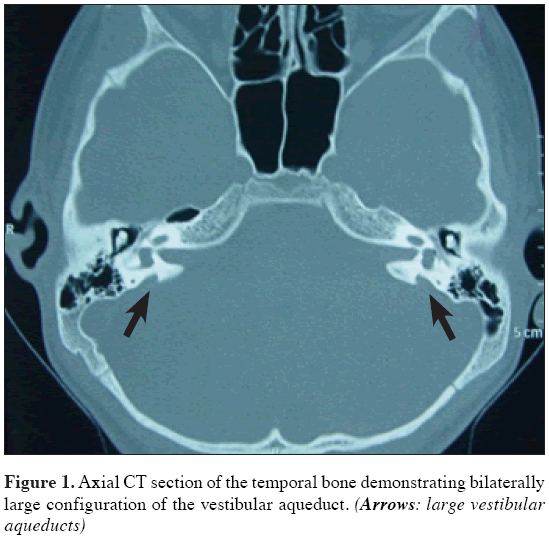
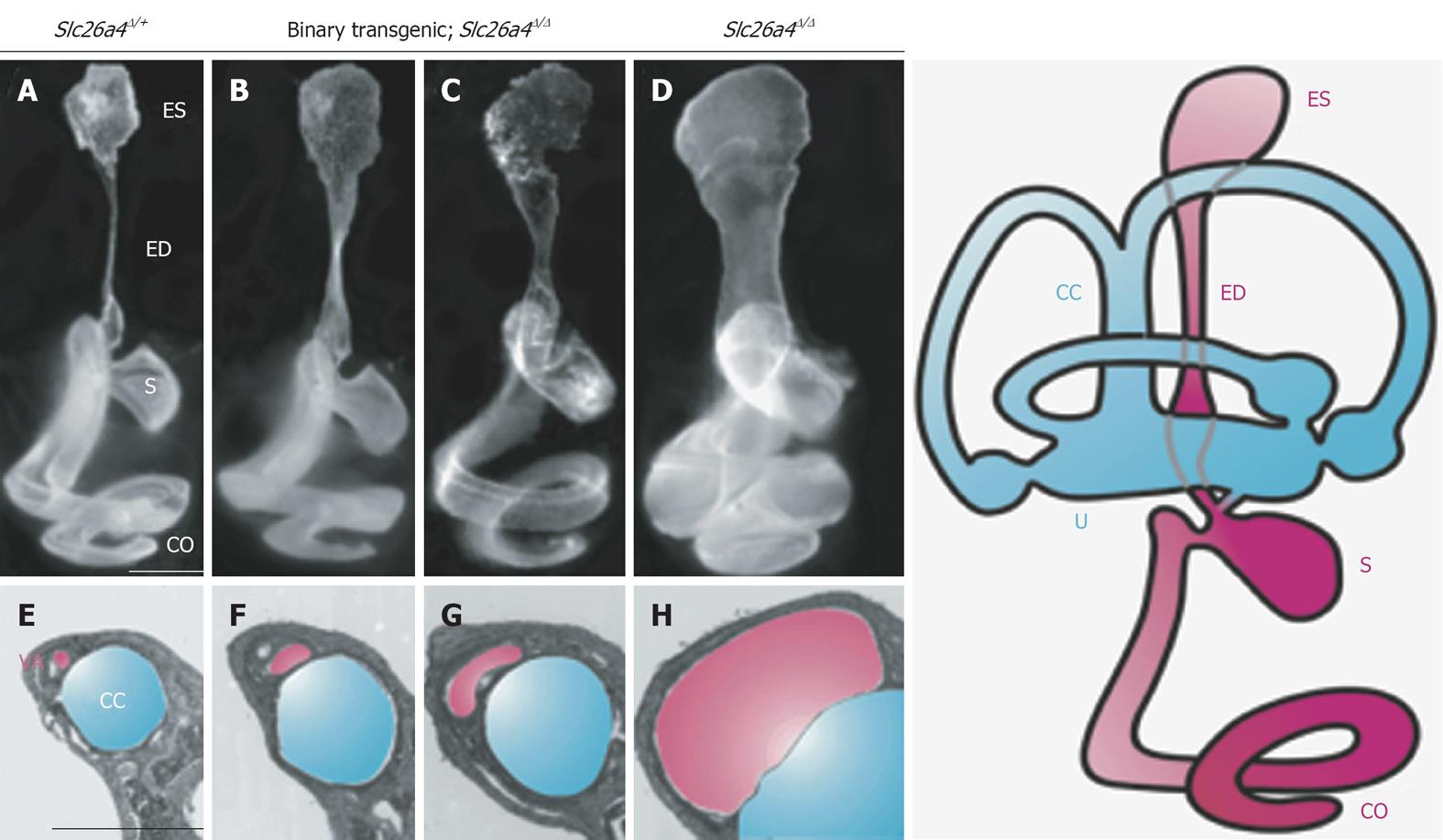
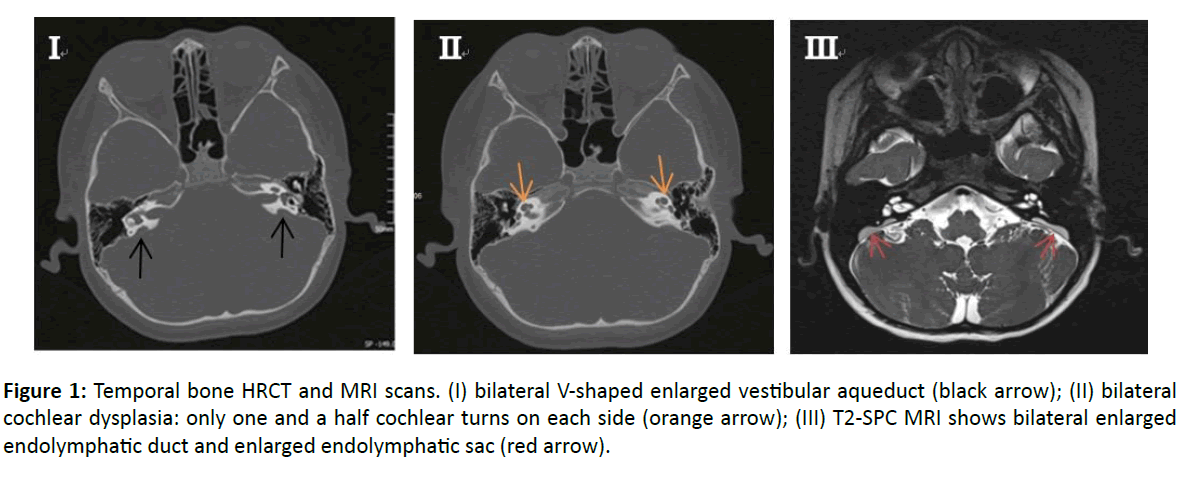
When a vestibular aqueduct is larger than normal it is known as a large vestibular aqueduct LVA or by the term used here enlarged vestibular aqueduct EVA. Hearing loss or balance symptoms associated with an EVA can occur when the endolymphatic duct and sac expand to fill the larger space see Figure. The enlarged vestibular aqueduct syndrome is one of the most common causes of congenital sensorineural hearing loss.
Large vestibular aqueduct syndrome LVAS large endolymphatic duct and sac syndrome LEDS. In their report they noted an association between enlargement of the vestibular aqueduct and sensorineural hearing loss SNHL. Enlarged vestibular aqueduct EVA syndrome is a common congenital inner ear malformation characterized by a vestibular aqueduct with a diameter larger.
If a vestibular aqueduct is enlarged the endolymphatic duct and sac usually grow large too. Jackler and De La Cruz.
It is manifested as enlargement of the bony canal of the vestibular aqueduct on computed tomography CT or enlargement of the endolymphatic sac visualized directly on magnetic resonance imaging MRI.
Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome EVAS Also known as Large Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome EVAS is a non-congenital syndromic form of hearing loss caused by an enlarged vestibular aqueduct usually with a diameter larger than 15mm Valvassori Clemis 1978. The functions of the endolymphatic duct and sac are not completely understood. Hearing loss or balance symptoms associated with an EVA can occur when the endolymphatic duct and sac expand to fill the larger space see Figure. ClinicalTrialsgov lists trials that are related to Enlarged vestibular aqueduct syndrome. Studies listed on the ClinicalTrialsgov website are listed for informational purposes only. If a vestibular aqueduct is enlarged the endolymphatic duct and sac usually grow large too. Pendred syndromenonsyndromic enlarged vestibular aqueduct PDSNSEVA comprises a phenotypic spectrum of sensorineural hearing loss SNHL that is usually congenital and often severe to profound although mild-to-moderate progressive hearing impairment also occurs vestibular dysfunction and temporal bone abnormalities bilateral enlarged vestibular aqueduct with or without cochlear hypoplasia. In their report they noted an association between enlargement of the vestibular aqueduct and sensorineural hearing loss SNHL. The condition is also known as a dilated vestibular aqueduct or a large vestibular aqueduct.
Jackler and De La Cruz. Studies listed on the ClinicalTrialsgov website are listed for informational purposes only. The enlarged vestibular aqueduct syndrome is one of the most common causes of congenital sensorineural hearing loss. Enlarged vestibular aqueduct EVA syndrome is a common congenital inner ear malformation characterized by a vestibular aqueduct with a diameter larger. Pendred syndromenonsyndromic enlarged vestibular aqueduct PDSNSEVA comprises a phenotypic spectrum of sensorineural hearing loss SNHL that is usually congenital and often severe to profound although mild-to-moderate progressive hearing impairment also occurs vestibular dysfunction and temporal bone abnormalities bilateral enlarged vestibular aqueduct with or without cochlear hypoplasia. Large vestibular aqueduct syndrome LVAS also known as enlarged vestibular aqueduct EVA or large endolymphatic sac anomaly LESA refers to the presence of congenital sensorineural hearing loss with an enlarged vestibular aqueduct due to enlargement of the endolymphatic duct. To determine the natural history of hearing loss in children with enlarged vestibular aqueduct EVA syndrome.





























Post a Comment for "Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome"