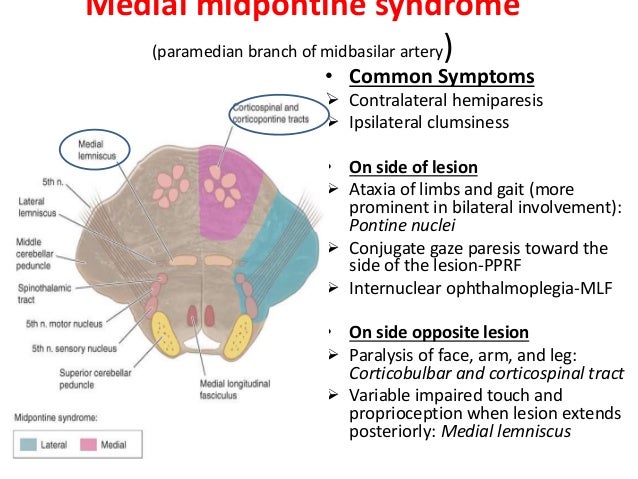
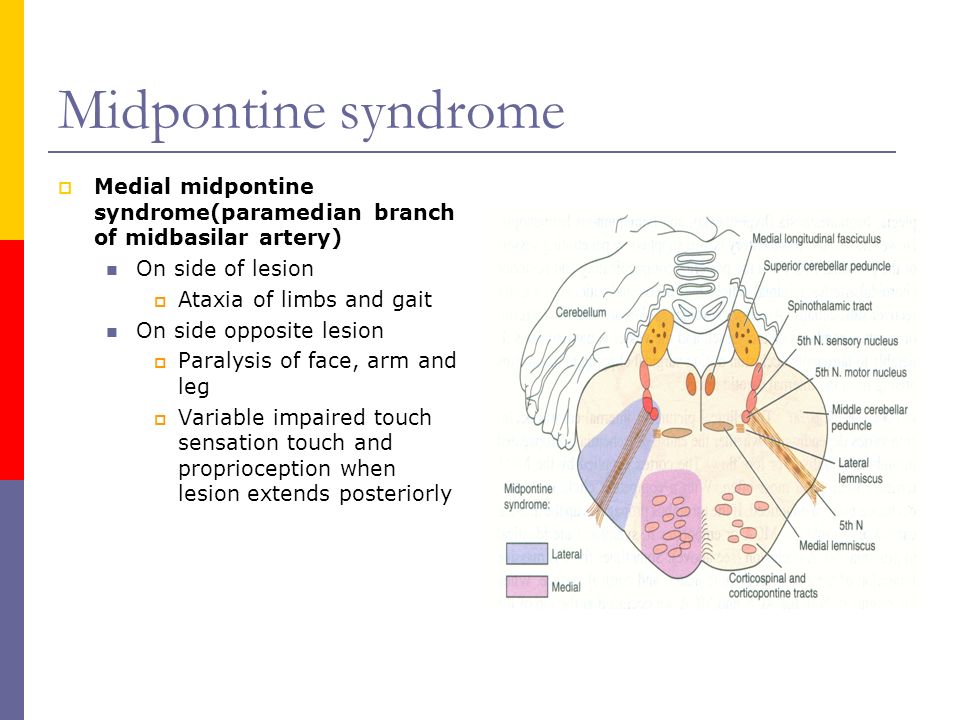
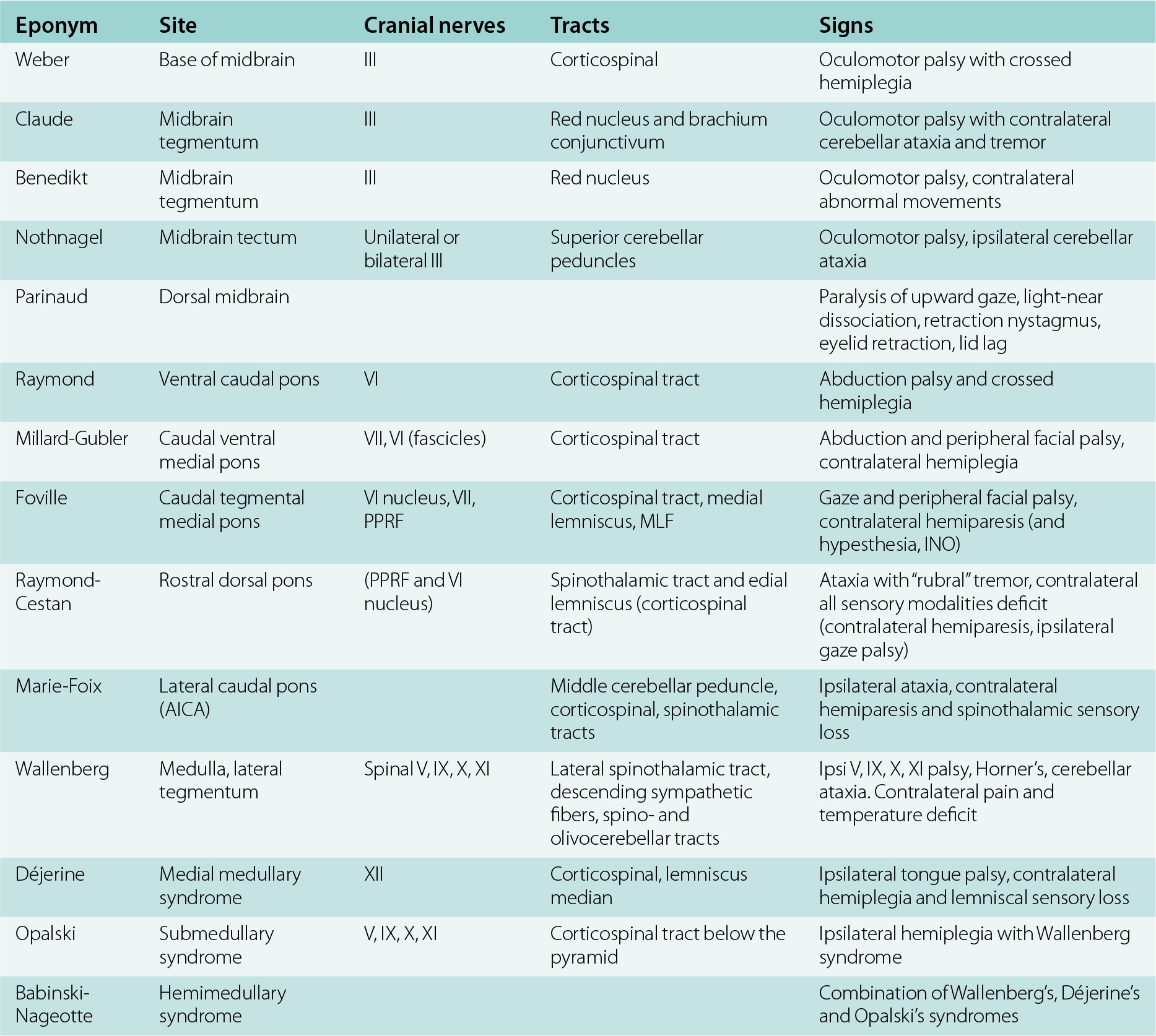
Medial Mid Pontine Syndrome
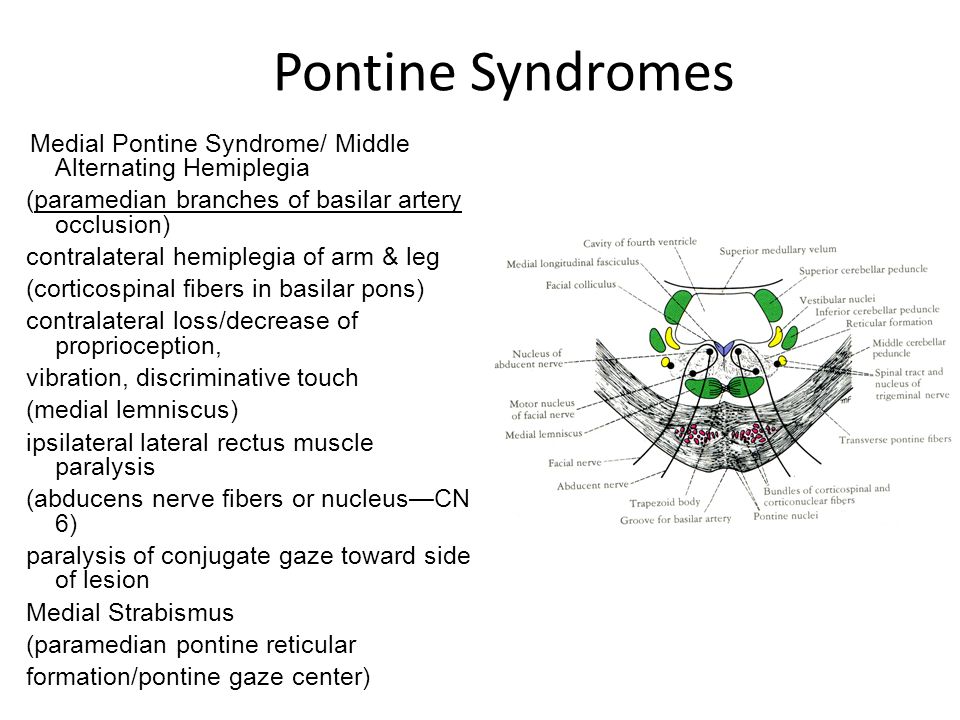
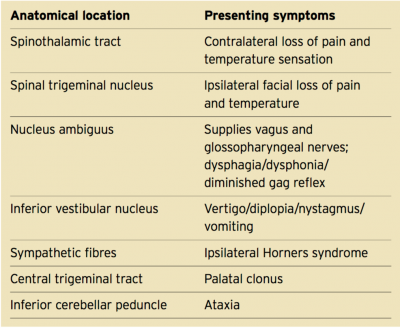
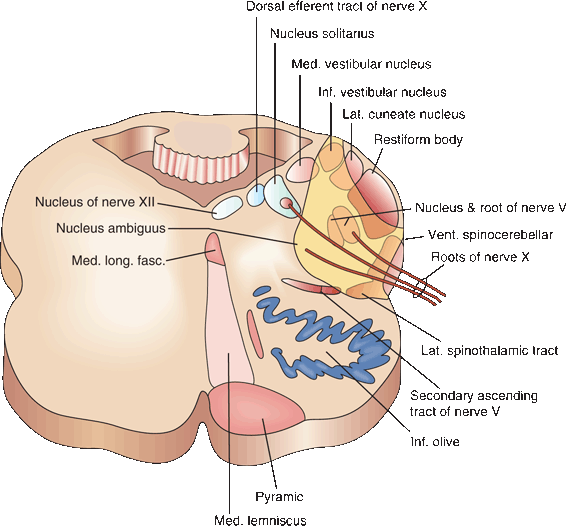
Medial mid pontine syndrome. Medial Pontine Syndrome This condition is also known as Fovilles syndrome caused by the blockage of the paramedian and the short circumferential branches of the basilar artery. 1618 It is characterized by simultaneous infarction of median paramedian lateral and dorsal areas of the medulla oblongata. The medial lemniscus car-.
Medial Mid-Pontine Syndrome d. To the pontine nuclei and then to the opposite cerebellum allowing coordination of planned. Httplyremilanblogspotca201203medial-inferior-pontine-syndromehtmlThese videos are designed for medical students studying for the USMLE step 1.
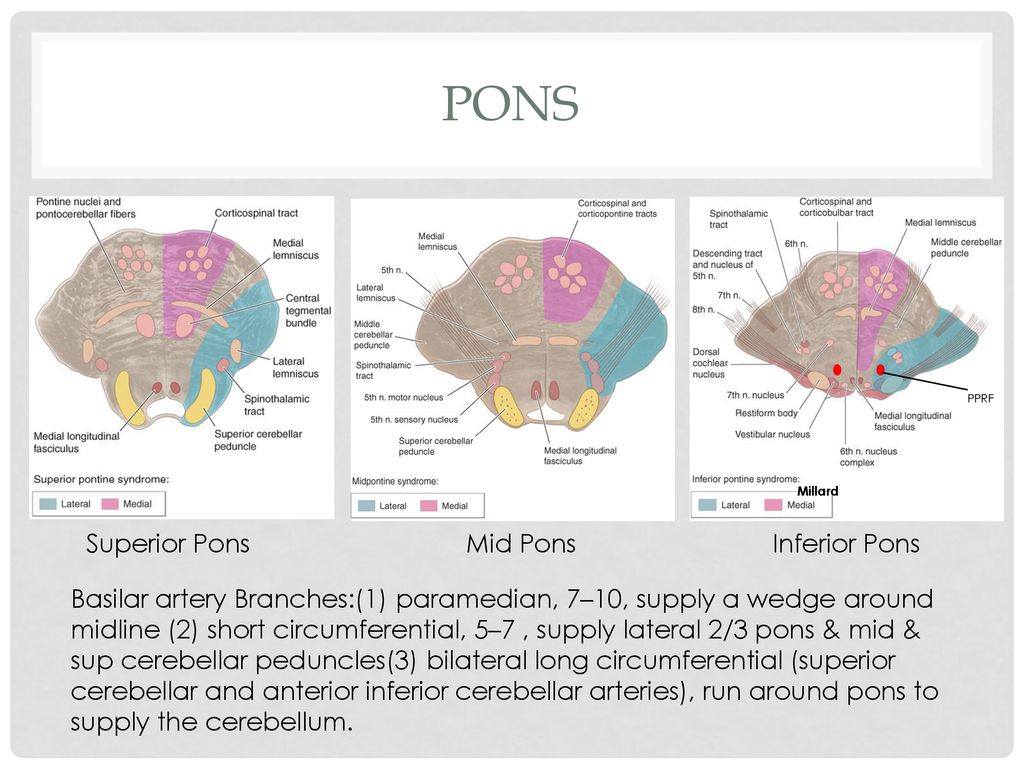
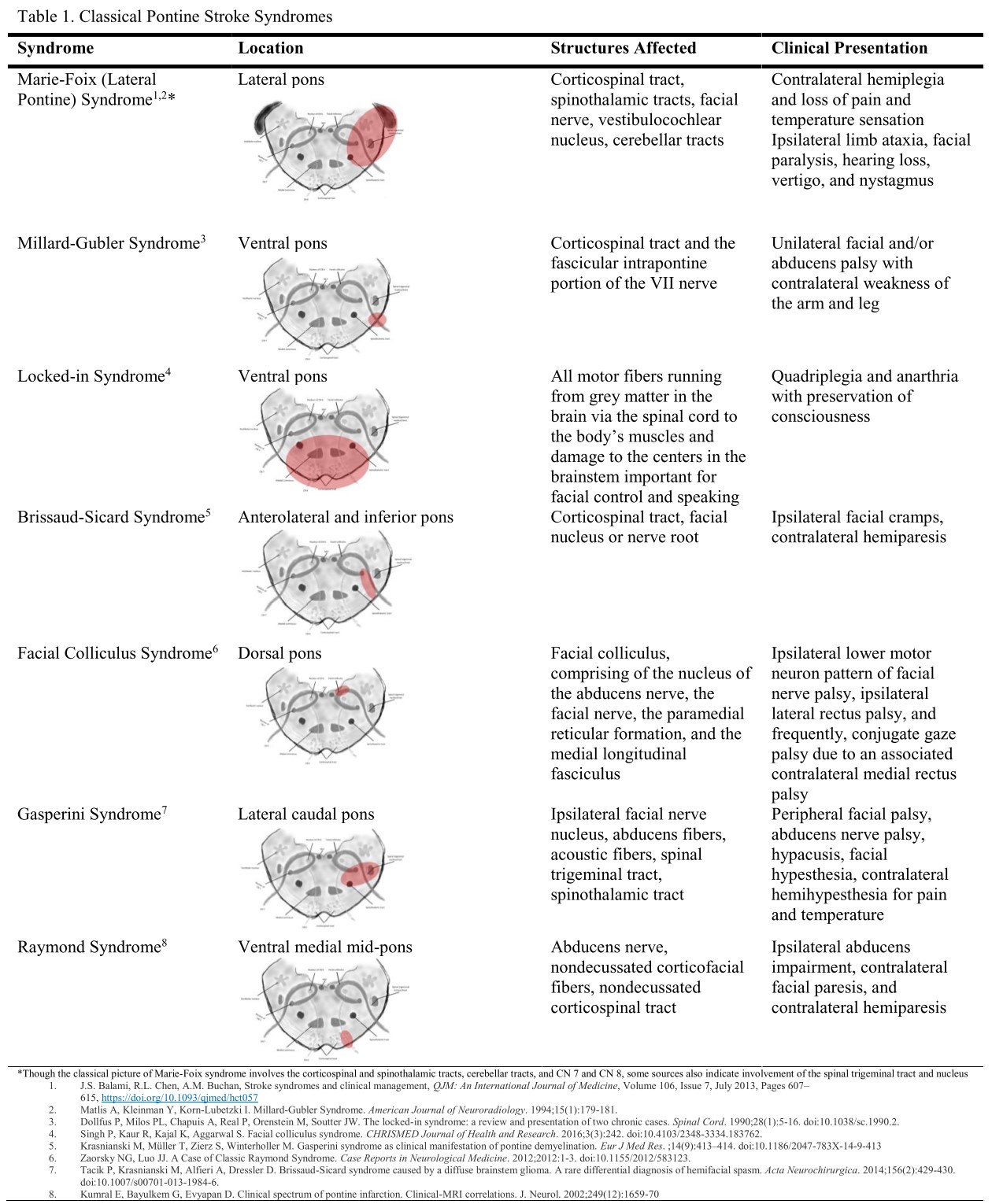
Clinical presentation There is a characteristic clinical picture1. The part of the brain affected is the pons. Upper dorsal pontine syndrome.
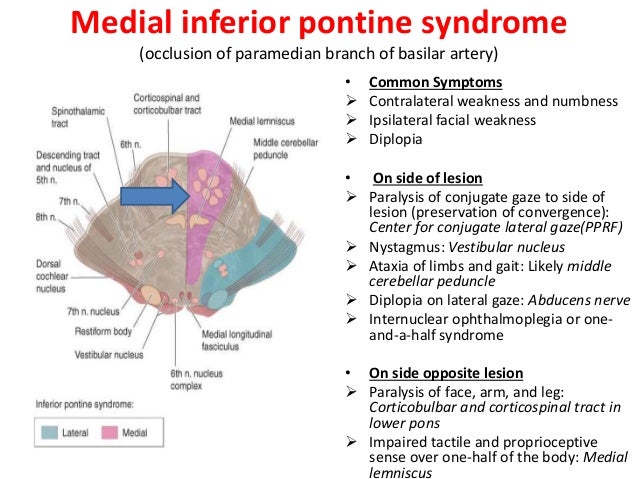
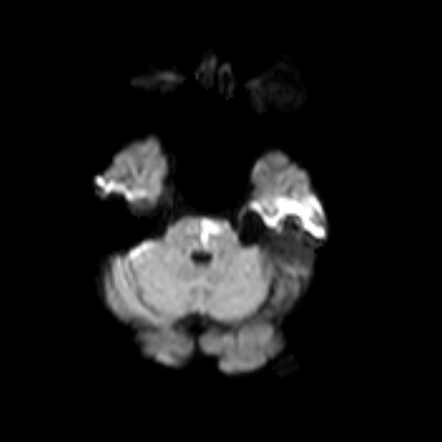
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging revealed a punctate area of acute ischemia in the right medial pontine mid-tegmentum. Inferior medial pontine syndrome also known as Foville syndrome is one of the brainstem stroke syndromes occurring when there is infarction of the medial inferior aspect of the pons due to occlusion of the paramedian branches of the basilar artery 1-3. The structures of the pons affected by the blockage are.
Lateral Mid-Pontine Syndrome e. Clinical findings are the following. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging revealed a punctate area of acute ischemia in the right medial pontine mid-tegmentum.
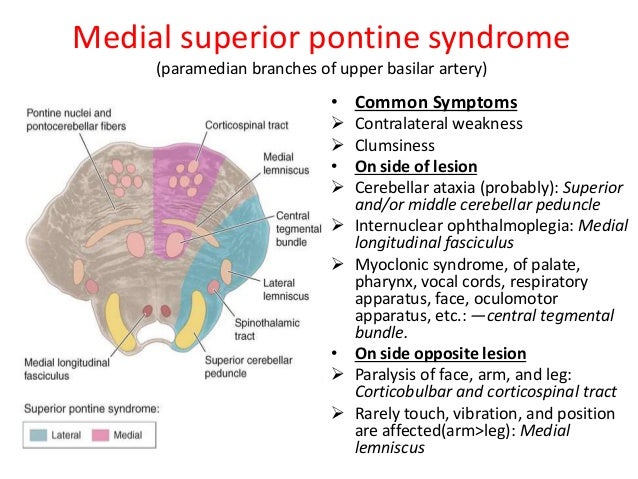
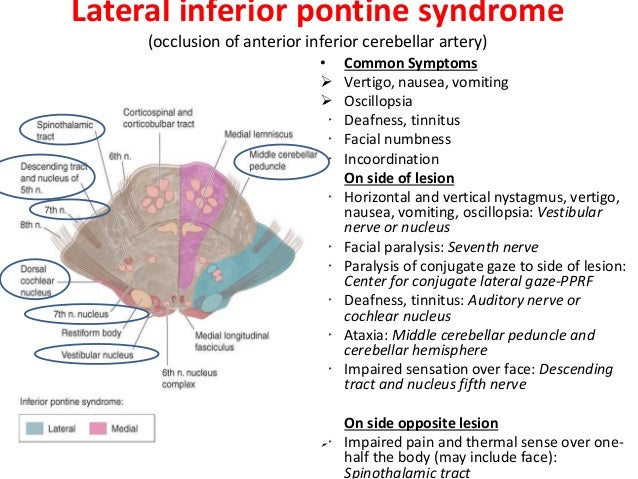
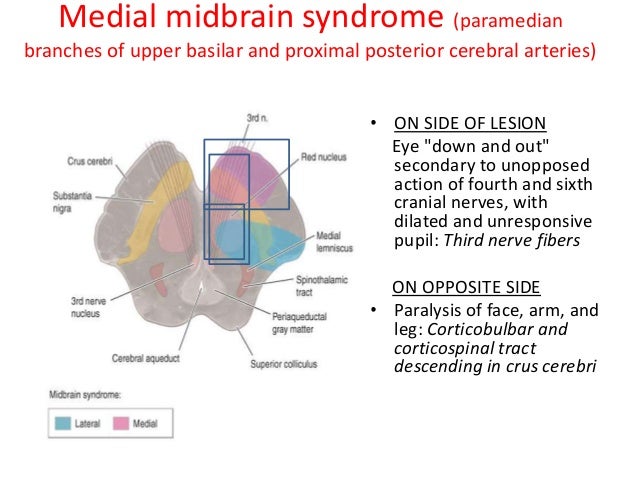
Occurs secondary to compressing tumor to the upper and medial portion of the pons or stoke affecting paramedian branches of the upper basilar artery. Lateral pontine syndrome also known as Marie-Foix syndrome or Marie-Foix-Alajouanine syndrome refers to one of the brainstem stroke syndromes of the lateral aspect of the pons. Medial superior pontine syndrome.
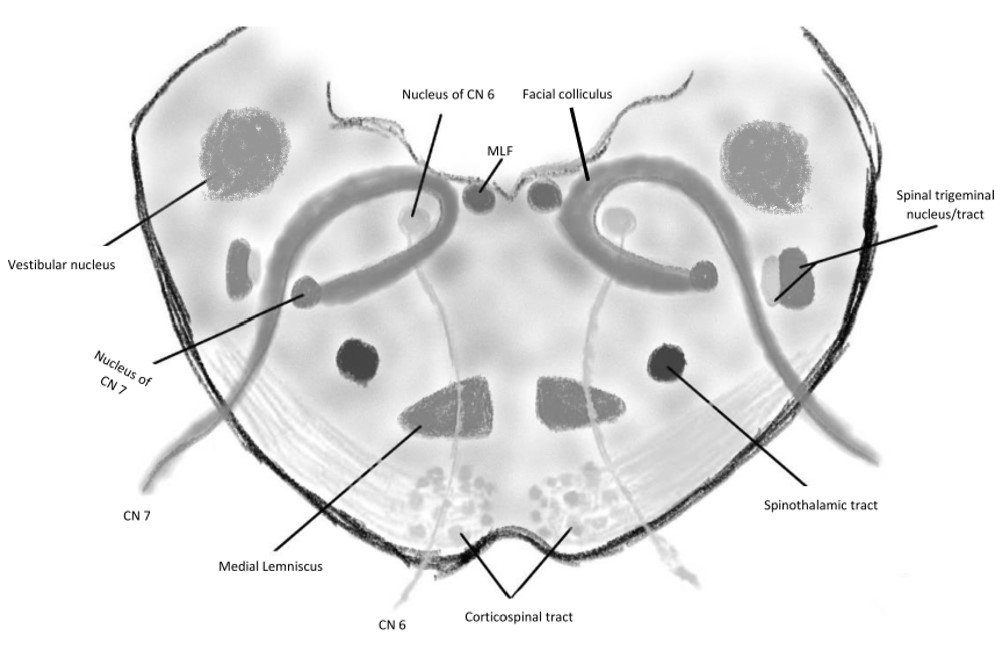
Ventral paramedian pontine lesion involving 6th and 7th fascicles and the pyramidal tract. Pontine Syndromes Raymond Cestan Syndrome.
363738 Thus supranuclear facial palsy with a sixth nerve palsy may be indicative of a paramedian pontine infarct.
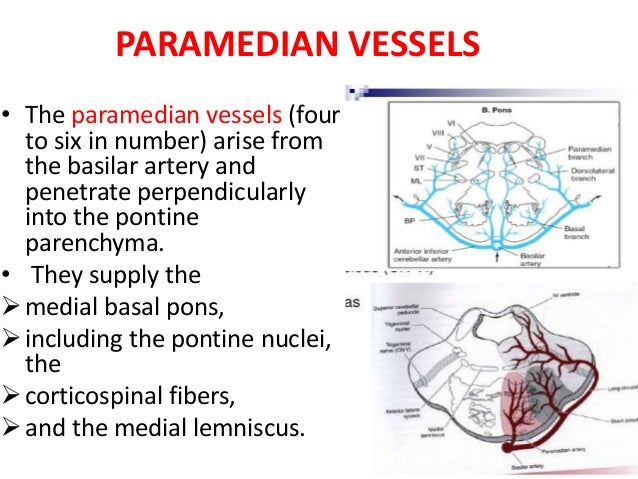
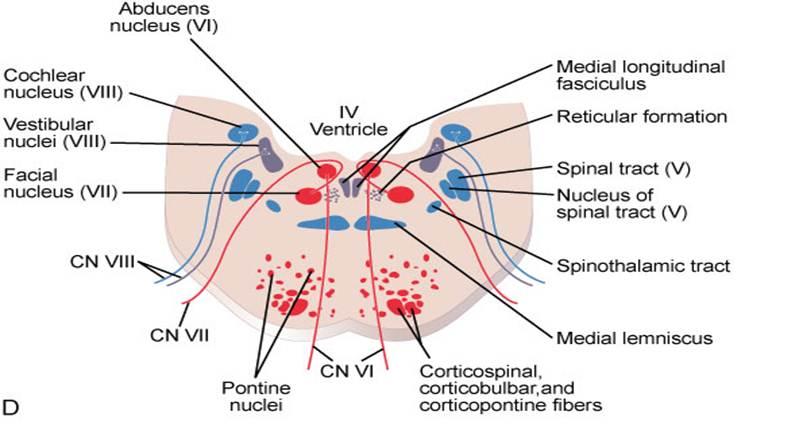
A lesion involving the abducens nerve fasciculus passing through the medial tegmentum to the basis pontis at the mid-pontine level can cause an isolated unilateral lateral rectus palsy. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging revealed a punctate area of acute ischemia in the right medial pontine mid-tegmentum. To the pontine nuclei and then to the opposite cerebellum allowing coordination of planned. 18 It can occur occasionally in associations with multiple brain stem strokes but rarely in isolation either simultaneously or. Httplyremilanblogspotca201203medial-inferior-pontine-syndromehtmlThese videos are designed for medical students studying for the USMLE step 1. Medial Pontine Syndrome This condition is also known as Fovilles syndrome caused by the blockage of the paramedian and the short circumferential branches of the basilar artery. Inferior medial pontine syndrome also known as Foville syndrome is one of the brainstem stroke syndromes occurring when there is infarction of the medial inferior aspect of the pons due to occlusion of the paramedian branches of the basilar artery 1-3. Lateral pontine syndrome also known as Marie-Foix syndrome or Marie-Foix-Alajouanine syndrome refers to one of the brainstem stroke syndromes of the lateral aspect of the pons. This infarction involves the following 1-3.
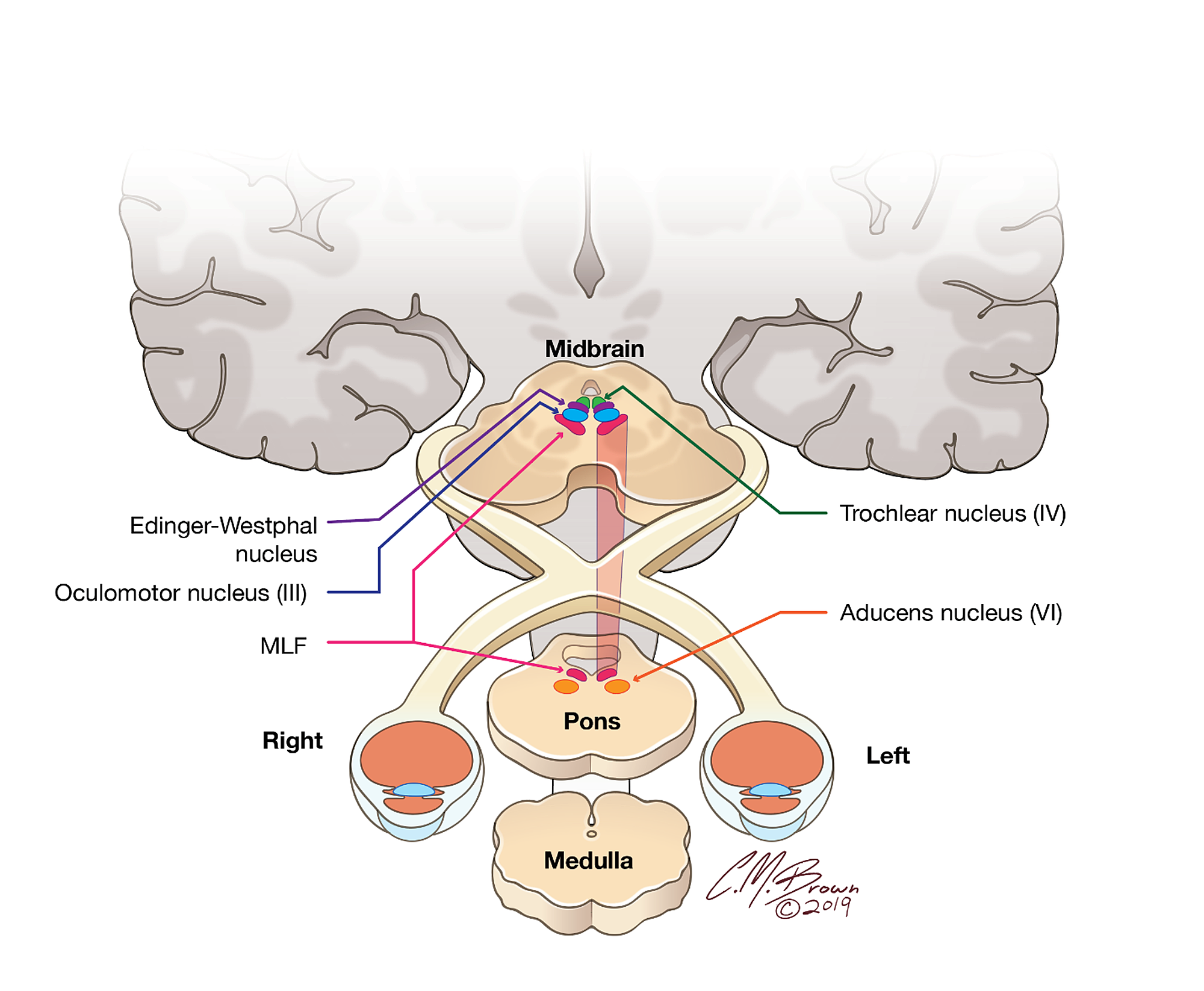
18 It can occur occasionally in associations with multiple brain stem strokes but rarely in isolation either simultaneously or. This infarction involves the following 1-3. Httplyremilanblogspotca201203medial-inferior-pontine-syndromehtmlThese videos are designed for medical students studying for the USMLE step 1. Medial longitudinal fasciculus is the main central connection for the oculomotor nerve and coordi-nates conjugate gaze. Medial Pontine Syndrome This condition is also known as Fovilles syndrome caused by the blockage of the paramedian and the short circumferential branches of the basilar artery. 1 VASCULAR LESIONS - MEDIAL MID-PONTINE SYNDROME. Lateral Inferior Pontine Syndrome c.











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-the-pons-3146161_FINAL-7cb45dbfe02944b797a73e222fc82f3f.gif)



/what-is-the-pons-3146161_FINAL-7cb45dbfe02944b797a73e222fc82f3f.gif)






Post a Comment for "Medial Mid Pontine Syndrome"