A Disease That Has A Steady Frequency Over Time In A Population Is
A disease that has a steady frequency over time in a population is. Although communicable diseases have declined in industrialised societies outbreaks of disease such as influenza gastroenteritis and hepatitis are still important. A particular locus on a chromosome and a given allele at that locus A population. Using this strategy the block of susceptible individuals is then immediately removed making it possible to eliminate an infectious disease such as measles from the entire population.
That an individual develops disease in a specified time period. In contrast to the prevalence the incidence reflects the number of new cases of disease and can be. All diseases of modernity exhibit the sine qua noncharacteristic of an increasing incidence over time because the environment continues to deviate further from the human EEA and individuals live longer within these novel environments.
To describe how often a disease or another health event occurs in a population different measures of disease frequency can be used. Hyperendemic refers to persistent high levels of disease occurrence. A population in which the numbers of people with and without the disease remain stable is known as a steady-state population.
In such theoretical circumstances the point prevalence of disease is approximately equal to the product of the incidence rate and the mean duration of disease ie. It is also known as the incidence density rate or person-time incidence rate when the denominator is the combined person-time of the population at risk the sum of the time duration of exposure across all persons exposed. A measure of the incidence rate of an event eg a disease or death in a population at risk over an observed period to time that directly incorporates time into the denominator.
The incidence rate is a measure of the frequency with which a disease or other incident occurs over a specified time period. The prevalence reflects the number of existing cases of a disease. Finally note that in.
For example if a doctor tells you that the 5-year CIR of disease X is 10 then this implies that you have a 10 risk of developing the disease over the next 5 years note that the term risk may also be described as the chance or likelihood of developing the disease. Specifically it is the fraction of all chromosomes in the population that carry that allele. Another related phrase context-sensitive half-time has been extensively used in the anaesthesia literature since most anaesthetics exhibit multiexponential disposition.
Sporadic refers to a disease that occurs infrequently and irregularly. Person-time is the sum of time that each person remains at risk for the disease or health outcome and under study observation.
In contrast to the prevalence the incidence reflects the number of new cases of disease and can be.
A person in the study can stop contributing person-time for. To describe how often a disease or another health event occurs in a population different measures of disease frequency can be used. In such theoretical circumstances the point prevalence of disease is approximately equal to the product of the incidence rate and the mean duration of disease ie. Length of time from diagnosis to recovery or death providing that prevalence is less than about 011. Finally note that in. The incidence rate is a measure of the frequency with which a disease or other incident occurs over a specified time period. Person-time is the sum of time that each person remains at risk for the disease or health outcome and under study observation. A measure of the incidence rate of an event eg a disease or death in a population at risk over an observed period to time that directly incorporates time into the denominator. The amount a particular disease present in a population over a period of time.
It is also known as the incidence density rate or person-time incidence rate when the denominator is the combined person-time of the population at risk the sum of the time duration of exposure across all persons exposed. Using this strategy the block of susceptible individuals is then immediately removed making it possible to eliminate an infectious disease such as measles from the entire population. A person in the study can stop contributing person-time for. In such theoretical circumstances the point prevalence of disease is approximately equal to the product of the incidence rate and the mean duration of disease ie. This strategy repeatedly vaccinates a defined age-cohort such as young children or the elderly in a susceptible population over time. It is also known as the incidence density rate or person-time incidence rate when the denominator is the combined person-time of the population at risk the sum of the time duration of exposure across all persons exposed. A particular locus on a chromosome and a given allele at that locus A population.








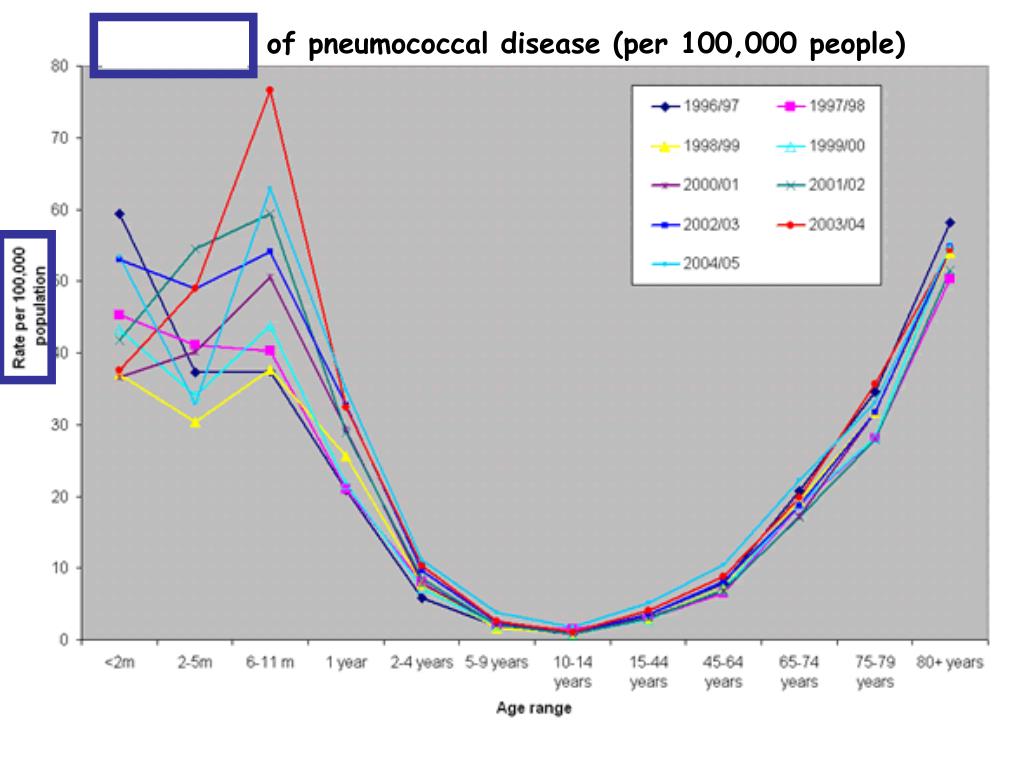

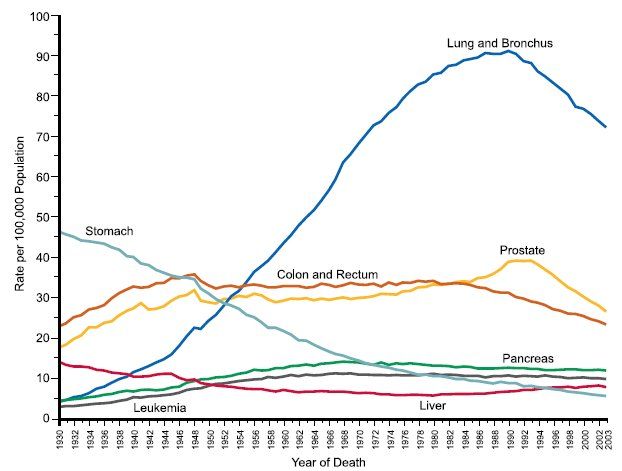

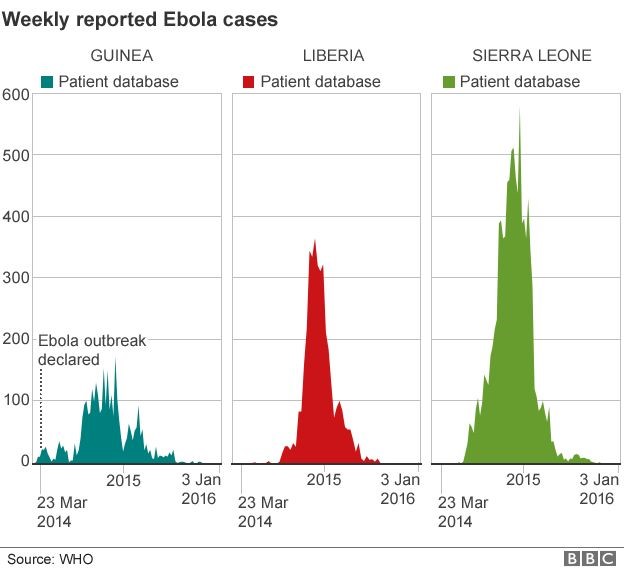









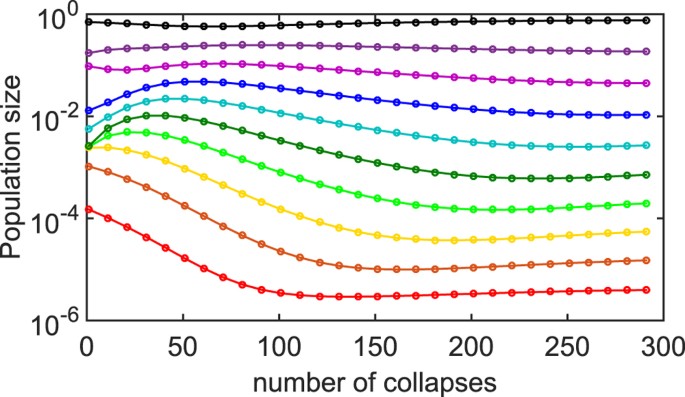

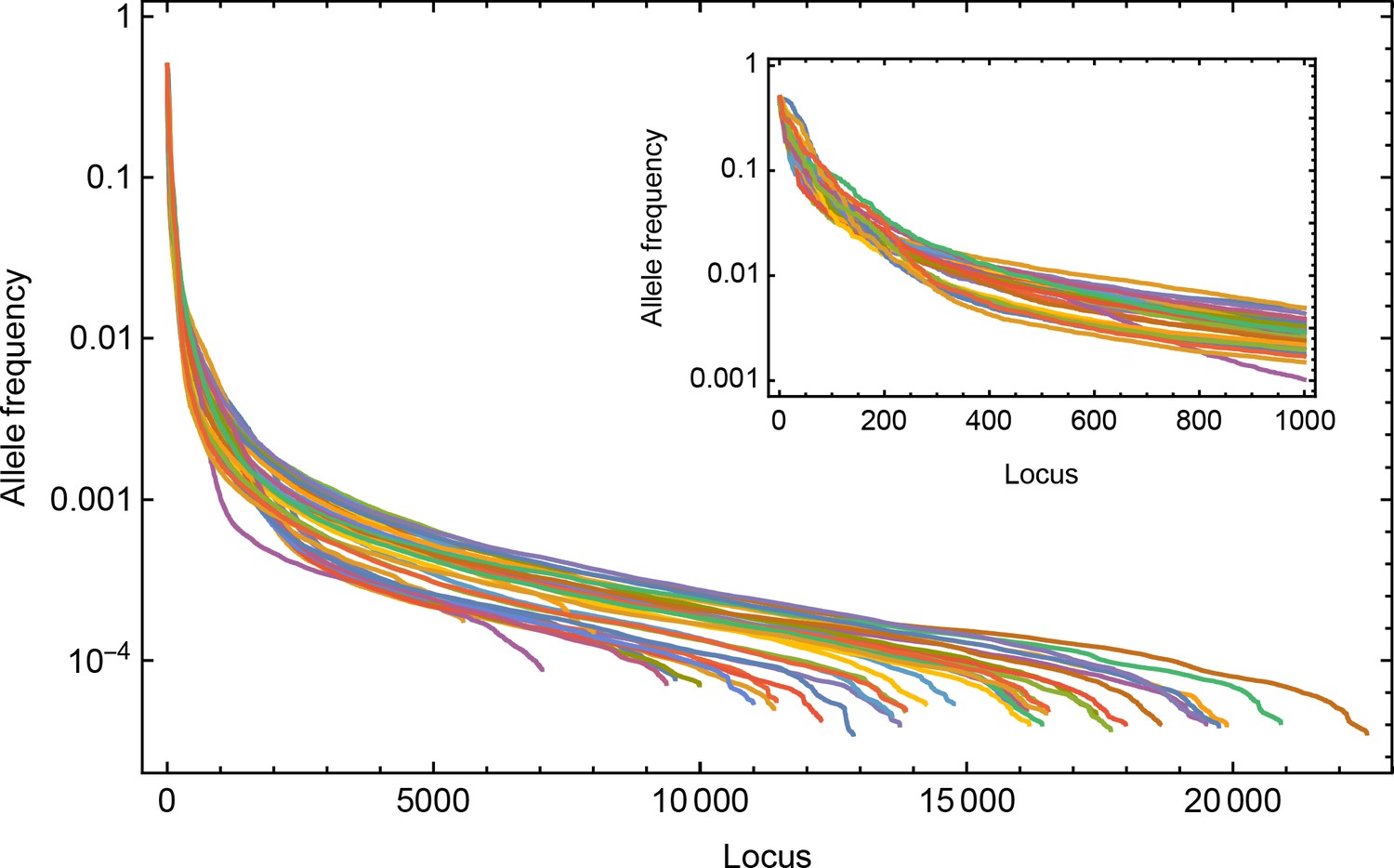

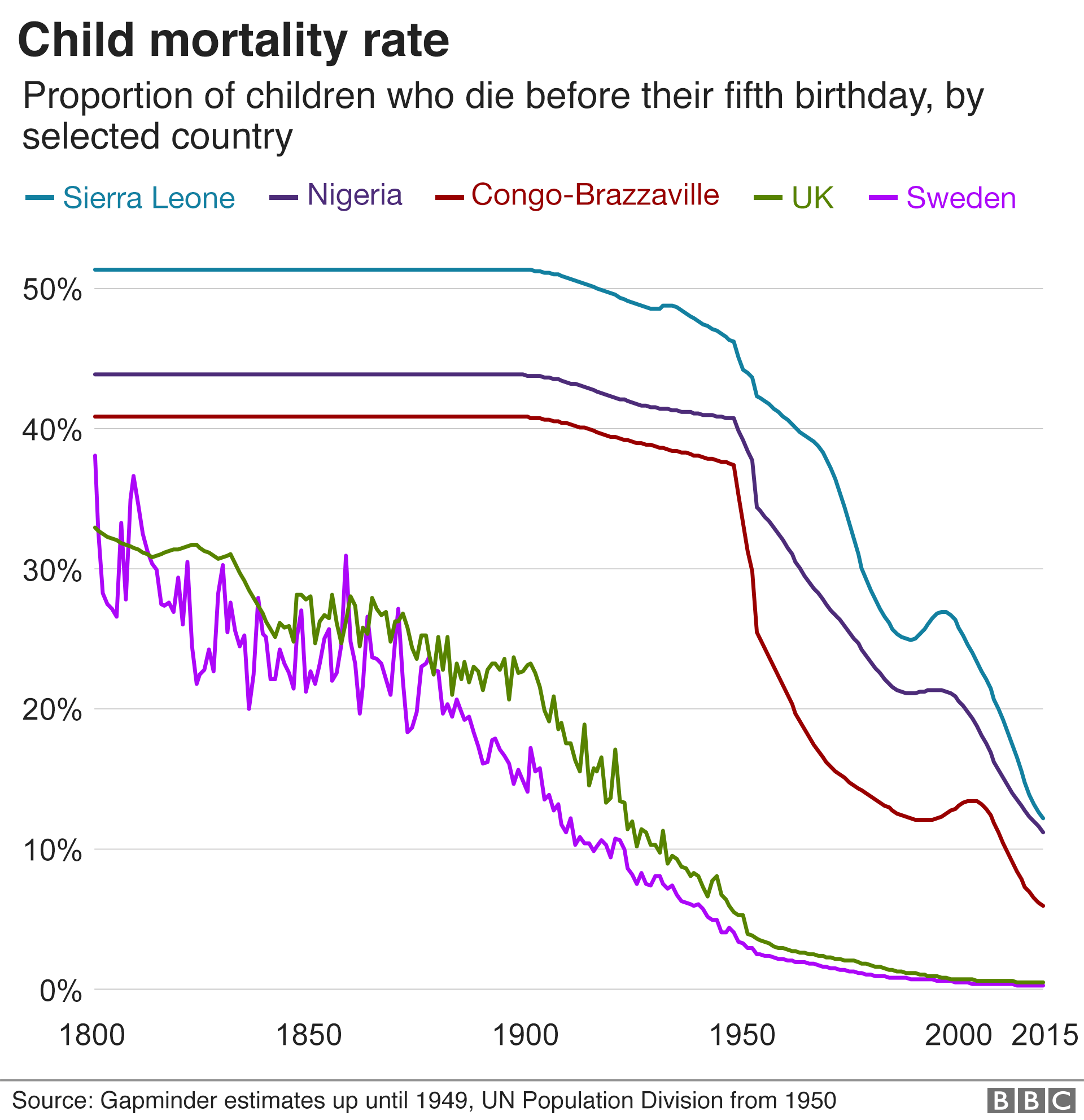


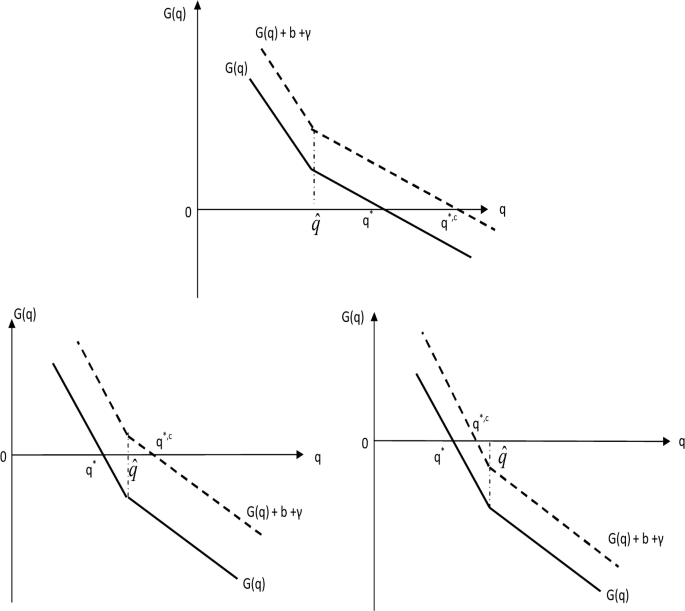





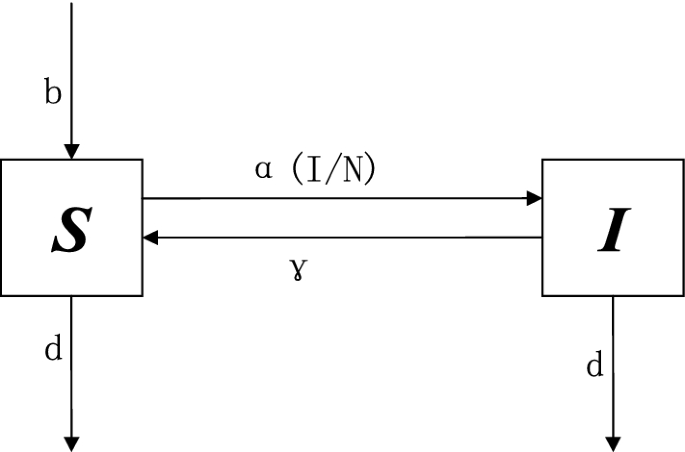
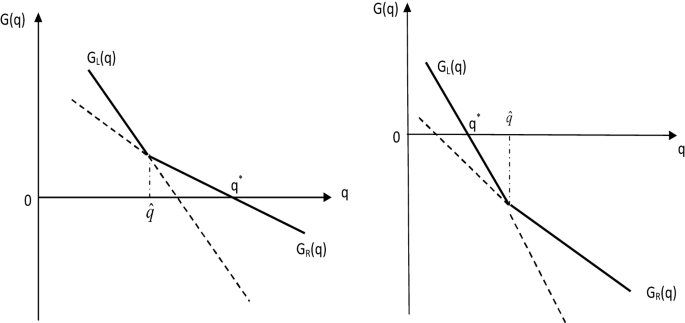

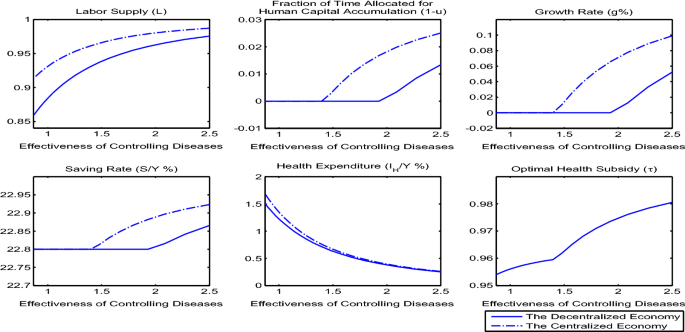


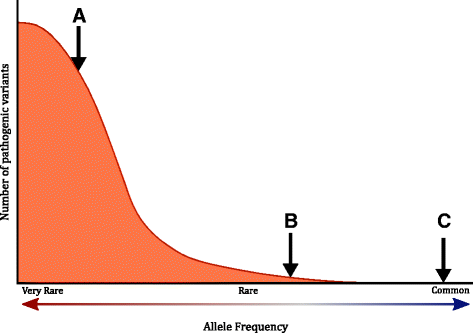
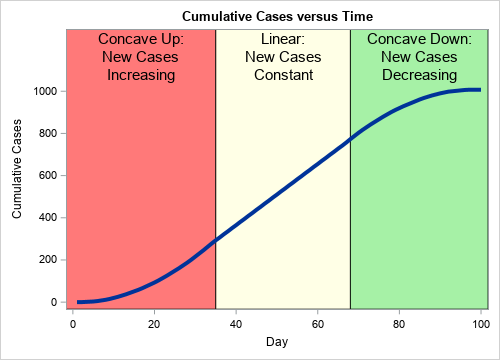
Post a Comment for "A Disease That Has A Steady Frequency Over Time In A Population Is"